Introduction to Deques
A deque, also known as a double-ended queue, is an ordered collection of items similar to the queue. It has two ends, a front and a rear, and the items remain positioned in the collection. What makes a deque different is the unrestrictive nature of adding and removing items. New items can be added at either the front or the rear. Likewise, existing items can be removed from either end. In a sense, this hybrid linear structure provides all the capabilities of stacks and queues in a single data structure.
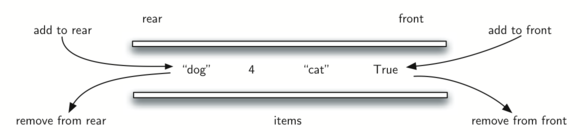
The Deque Abstract Data Type
The deque abstract data type is defined by the following structure and operations. A deque is structured, as described above, as an ordered collection of items where items are added and removed from either end, either front or rear. The deque operations are given below.
Deque()creates a new deque that is empty. It needs no parameters and returns an empty deque.add_front(item)adds a new item to the front of the deque. It needs the item and returns nothing.add_rear(item)adds a new item to the rear of the deque. It needs the item and returns nothing.remove_front()removes the front item from the deque. It needs no parameters and returns the item. The deque is modified.remove_rear()removes the rear item from the deque. It needs no parameters and returns the item. The deque is modified.is_empty()tests to see whether the deque is empty. It needs no parameters and returns a boolean value.size()returns the number of items in the deque. It needs no parameters and returns an integer.
As an example, if we assume that d is a deque that has been created
and is currently empty, the table below shows the results
of a sequence of deque operations.
| Deque Operation | Deque Contents | Return Value |
|---|---|---|
d.is_empty() |
[] |
True |
d.add_rear(4) |
[4] |
|
d.add_rear('dog') |
['dog', 4] |
|
d.add_front('cat') |
['dog', 4, 'cat'] |
|
d.add_front(True) |
['dog', 4,'cat', True] |
|
d.size() |
['dog', 4, 'cat', True] |
4 |
d.is_empty() |
['dog', 4, 'cat', True] |
False |
d.add_rear(8.4) |
[8.4, 'dog', 4, 'cat',True] |
|
d.remove_rear() |
['dog', 4, 'cat', True] |
8.4 |
d.remove_front() |
`['dog', 4, 'cat'] | True |