Parse Trees
With the implementation of our tree data structure complete, we now look at an example of how a tree can be used to solve some real problems. In this section we will look at parse trees. Parse trees can be used to represent real-world constructions like sentences or mathematical expressions.
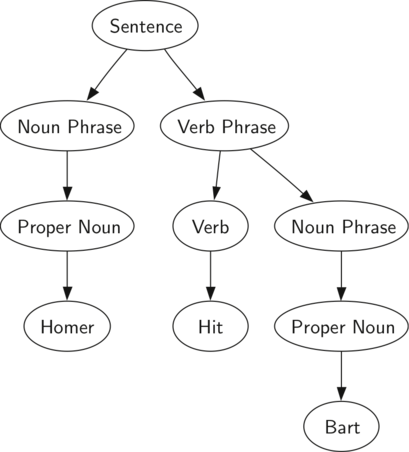
The diagram below shows the hierarchical structure of a simple sentence. Representing a sentence as a tree structure allows us to work with the individual parts of the sentence by using subtrees.
We can also represent a mathematical expression such as as a parse tree, as shown below.
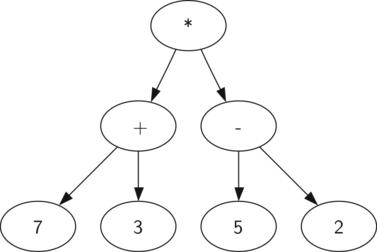
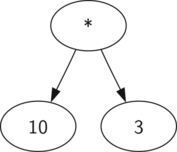
We have already looked at fully parenthesized expressions, so what do we know about this expression? We know that multiplication has a higher precedence than either addition or subtraction. Because of the parentheses, we know that before we can do the multiplication we must evaluate the parenthesized addition and subtraction expressions. The hierarchy of the tree helps us understand the order of evaluation for the whole expression. Before we can evaluate the top-level multiplication, we must evaluate the addition and the subtraction in the subtrees. The addition, which is the left subtree, evaluates to 10. The subtraction, which is the right subtree, evaluates to 3. Using the hierarchical structure of trees, we can simply replace an entire subtree with one node once we have evaluated the expressions in the children. Applying this replacement procedure gives us the simplified tree shown below.
In the rest of this section we are going to examine parse trees in more detail. In particular we will look at how to build a parse tree from a fully parenthesized mathematical expression, and how to evaluate the expression stored in a parse tree.
The first step in building a parse tree is to break up the expression string into a list of tokens. There are four different kinds of tokens to consider: left parentheses, right parentheses, operators, and operands. We know that whenever we read a left parenthesis we are starting a new expression, and hence we should create a new tree to correspond to that expression. Conversely, whenever we read a right parenthesis, we have finished an expression. We also know that operands are going to be leaf nodes and children of their operators. Finally, we know that every operator is going to have both a left and a right child.
Using the information from above we can define four rules as follows:
- If the current token is a
'(', add a new node as the left child of the current node, and descend to the left child. - If the current token is in the list
['+','-','/','*'], set the root value of the current node to the operator represented by the current token. Add a new node as the right child of the current node and descend to the right child. - If the current token is a number, set the root value of the current node to the number and return to the parent.
- If the current token is a
')', go to the parent of the current node.
Before writing the Python code, let’s look at an example of the rules
outlined above in action. We will use the expression . We
will parse this expression into the following list of character tokens
['(', '3', '+', '(', '4', '*', '5' ,')',')']. Initially we will
start out with a parse tree that consists of an empty root node.
The figures below illustrate the structure and contents
of the parse tree, as each new token is processed.

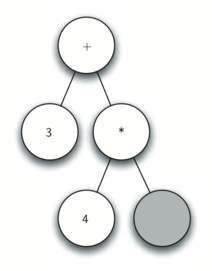
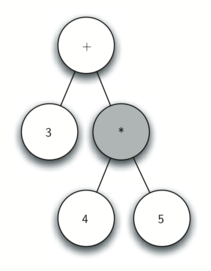
Using the above, let’s walk through the example step by step:
- Create an empty tree.
- Read ( as the first token. By rule 1, create a new node as the left child of the root. Make the current node this new child.
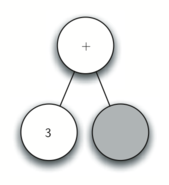
- Read 3 as the next token. By rule 3, set the root value of the current node to 3 and go back up the tree to the parent.
- Read + as the next token. By rule 2, set the root value of the current node to + and add a new node as the right child. The new right child becomes the current node.
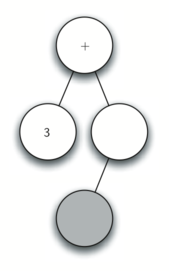
- Read a ( as the next token. By rule 1, create a new node as the left child of the current node. The new left child becomes the current node.
- Read a 4 as the next token. By rule 3, set the value of the current node to 4. Make the parent of 4 the current node.
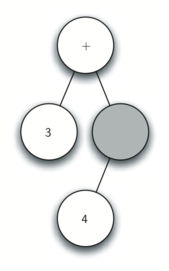
- Read * as the next token. By rule 2, set the root value of the current node to * and create a new right child. The new right child becomes the current node.
- Read 5 as the next token. By rule 3, set the root value of the current node to 5. Make the parent of 5 the current node.
- Read ) as the next token. By rule 4 we make the parent of * the current node.
- Read ) as the next token. By rule 4 we make the parent of + the current node. At this point there is no parent for + so we are done.
From the example above, it is clear that we need to keep track of the current node as well as the parent of the current node. A simple solution to keeping track of parents as we traverse the tree is to use a stack. Whenever we want to descend to a child of the current node, we first push the current node on the stack. When we want to return to the parent of the current node, we pop the parent off the stack.
Using the rules described above, along with the stack and binary tree abstract data types, we are now ready to write a Python function to create a parse tree. The code for our parse tree builder is presented below.
import operator
OPERATORS = {
'+': operator.add,
'-': operator.sub,
'*': operator.mul,
'/': operator.truediv
}
LEFT_PAREN = '('
RIGHT_PAREN = ')'
def build_parse_tree(expression):
tree = {}
stack = [tree]
node = tree
for token in expression:
if token == LEFT_PAREN:
node['left'] = {}
stack.append(node)
node = node['left']
elif token == RIGHT_PAREN:
node = stack.pop()
elif token in OPERATORS:
node['val'] = token
node['right'] = {}
stack.append(node)
node = node['right']
else:
node['val'] = int(token)
parent = stack.pop()
node = parent
return tree
The four rules for building a parse tree are coded as the four clauses
of the if statement above. In each case you can see that the code implements
the rule.
Now that we have built a parse tree, we can write a function to evaluate it, returning the numerical result. To write this function, we will make use of the hierarchical nature of the tree to write an algorithm that evaluates a parse tree by recursively evaluating each subtree.
A natural base case for recursive algorithms that operate on trees is to check
for a leaf node. In a parse tree, the leaf nodes will always be operands.
Since numerical objects like integers and floating points require no further
interpretation, the evaluate function can simply return the value stored in
the leaf node. The recursive step that moves the function toward the base case
is to call evaluate on both the left and the right children of the current
node. The recursive call effectively moves us down the tree, toward a leaf
node.
To put the results of the two recursive calls together, we can simply apply the operator stored in the parent node to the results returned from evaluating both children. In the example from above we see that the two children of the root evaluate to themselves, namely 10 and 3. Applying the multiplication operator gives us a final result of 30.
The code for a recursive evaluate function is shown below. First, we obtain
references to the left and the right children of the current node. If both the
left and right children evaluate to None, then we know that the current node
is really a leaf node. If the current node is not a leaf node, look up the
operator in the current node and apply it to the results from recursively
evaluating the left and right children.
To implement the arithmetic, we use a dictionary with the keys
'+', '-', '*', and '/'. The values stored in the dictionary are
functions from Python’s operator module. The operator module provides us
with the functional versions of many commonly used operators. When we
look up an operator in the dictionary, the corresponding function object
is retrieved. Since the retrieved object is a function, we can call it
in the usual way function(param1, param2). So the lookup
OPERATORS['+'](2, 2) is equivalent to operator.add(2, 2).
def evaluate(tree):
try:
operate = OPERATORS[tree['val']]
return operate(evaluate(tree['left']), evaluate(tree['right']))
except KeyError:
# no left or no right, so is a leaf - our base case
return tree['val']
Finally, we will trace the evaluate function on the parse tree we created
above. When we first call evaluate, we pass the root of the entire tree as
the parameter parse_tree. Then since the left and right children exist, we
look up the operator in the root of the tree, which is '+', and which maps
to the operator.add function. As usual for a Python function call, the first
thing Python does is to evaluate the parameters that are passed to the
function. In this case both parameters are recursive function calls to our
evaluate function. Using left-to-right evaluation, the first recursive call
goes to the left. In the first recursive call the evaluate function is given
the left subtree. We find that the node has no left or right children, so we
are in a leaf node. When we are in a leaf node we just return the value stored
in the leaf node as the result of the evaluation. In this case we return the
integer 3.
At this point we have one parameter evaluated for our top-level call to
operator.add. But we are not done yet. Continuing the left-to-right
evaluation of the parameters, we now make a recursive call to evaluate
the right child of the root. We find that the node has both a left and a
right child so we look up the operator stored in this node, '*', and
call this function using the left and right children as the parameters.
At this point you can see that both recursive calls will be to leaf
nodes, which will evaluate to the integers four and five respectively.
With the two parameters evaluated, we return the result of
operator.mul(4, 5). At this point we have evaluated the operands for
the top level '+' operator and all that is left to do is finish the
call to operator.add(3, 20). The result of the evaluation of the entire
expression tree for is 23.